Action manager
Action manager is the core service in workflow execution process.
Glossary:
Action/Connector- defenition of any action that should produce a useful resultWorkflow- a sequence of activities that carry out a processAction Inputor simplyInput- incoming data for actionAction Outputor simplyOutput- the result of the actionAction Settings- settings and instructions for executing an actionAction Credentials- credentials provided for the actionWorkflowStorage- an entity that characterizes the progress of a particular workflowWorkflow Taskor simplyTask- an entity that contains result of executed action:input,output,settings,parent_storage_idWorkflow Options- meta-data transferred from action manager to action executor and back to identify the workflow storage and the executable actionFlow controller action- action which determine the order in which instructions or statements are executedAction storage- storage for keepingWorkflow StorageandWorkflow TaskAction manager- action orchestratorHealthAnalyzer- statistics and workflow status generatorExecution Strategy- a strategy for executing a specific type of action in a workflow, based on its action typeNext Action Handler- it is a handler responsible for managing the logic associated with selecting the subsequent action to be executed in a workflow.Action Executor- abstract component which can execute specific action
HLD:
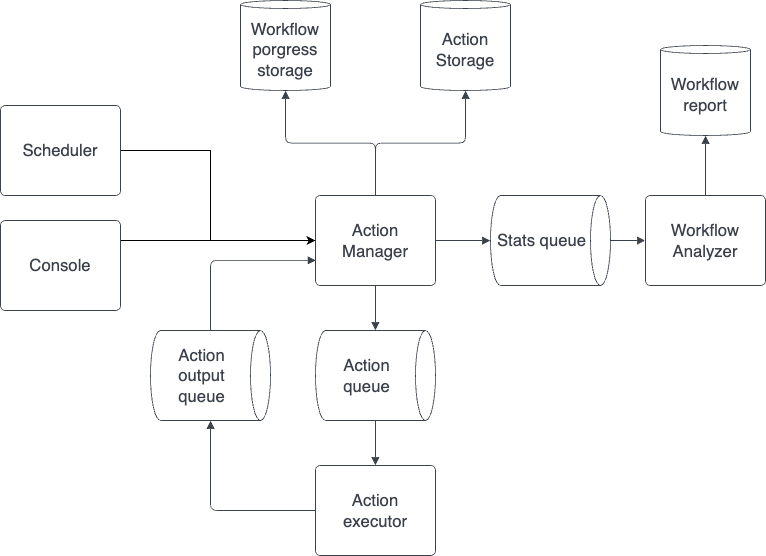
Concepts:
Every action has it's own action type. Actions are grouped together based on ther action type into groups:
1) Common Group
2) Microsoft Group
3) Playwright Group
4) ...
Each group of actions is executed on its own Action executor.
But there is specif group of action, called flow contollers. This group contains condition, loop and nested actions. They are executing on the Action Manager level, because they control how workflow should behave. From this emerges the concept of Execution strategy.
Currently there are 5 execution strategies:
Common strategy- strategy for executing all actions that are not part of theflow controllers.Common strategy does not only execute common group actions, although it has a similar name.
Conditional strategy- execute condition action to determine execution branchLoop strategy- determine amount of action to be execute and start executing themSingle execution strategy- strategy for executing single action outside of workflowNested strategy- strategy for executing action with nested acitons
After each completion of an action, the action manager updates the result and gets actions using different handlers of the next action
Next action handler - These are the strategies for handling the result of an action, depending on their type. That is, if the execution strategy decides how the action should be executed, the next action handler decides how to update the action progress and which action should be executed next.
Currently there are 4 next action handler:
Common handler- get next action in workflowConditional handler- get next action inside condition scopeLoop handler- get next action in loopSingle action- terminate execution
Description
The Action Manager serves as the central orchestrator for actions within a workflow. It initializes the workflow, executes actions, manages control flow, and ensures the overall progress and completion of the workflow.
Here is an overview of how it works:
1) Workflow Initialization: When a new workflow starts, the Action Manager initializes the workflow storage. This storage entity keeps track of the progress and state of the workflow.
2) Workflow Options: The Action Manager generates workflow options, which contain meta-information about the running workflow. This includes details such as the workflow id, customer id, and whether the workflow is running in test mode, current executing action id and task id, flow controllers stack
3) Execution Strategy: The Action Manager employs an execution strategy that is specific to the type of action being executed. This strategy defines how the action should be executed and handles any necessary interactions with external services or resources. The execution strategy utilizes the action's settings, input data, and credentials to perform the action and generate an output.
4) Handling Next Actions: After executing an action, the Action Manager determines the next action to be executed in the workflow. It relies on the Next Action Handler, which manages the logic for selecting the subsequent action based on the workflow's context and progress. The handler considers factors such as the current action's status and the presence of flow controller actions that determine the workflow's control flow.
5) Flow Controller: If an action fails and there are flow controllers in the workflow, the Action Manager attempts to find a loop flow controller to continue the iterations. It ensures that the workflow follows the desired control flow defined by the flow controllers. If no next action is available and there are no more flow controllers, the workflow execution is considered complete.
6) Workflow Statistics and Health Analysis: The Action Manager interacts with the Health Analyzer to generate statistics and analyze the overall health of the workflow. This includes collecting data on the execution status of actions, tracking errors or failures, and providing insights into the workflow's progress.
7) Workflow Completion: When the workflow execution is finished, the Action Manager handles the finalization process. It logs the completion status, adds a finalize job to the workflow statistics queue, and destroys the workflow storage.